PageStream gives you a blank page on which to mix text and graphics to create a finished page design. Text and graphics can be imported from other sources or created directly in PageStream and then arranged on the page. PageStream allows you to combine text and graphics without restrictions. It has a What-You-See-Is-What-You-Get, or WYSIWYG display, so that you will know what your document will look like before it is printed.
File Menu | Edit Menu | Layout Menu | Type Menu | Object Menu | Scripts Menu | Window Menu
Document Window | Navigator
| Toolbar | Toolbox
| Edit Palette
Color Palette | Style
Palette | Script Palette | Layer Palette | Page
Palette | Document Palette
New
Creates a new PageStream document. Opens a dialog box allowing
you to set the document name, the page size and orientation of
the default master page, the margin and column guides, and the
double-sided and facing pages modes.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > Creating a New Document
Open
Opens an existing PageStream document.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > Opening a Document
Open
Recent
Opens a recent PageStream document.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > Opening a Document > Recent documents
Append
Appends an existing PageStream document to the current one in
the active document window.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > Opening a Document > Appending a document
Close
Closes the document in the active document window.
Save
Saves the document in the active document window. This will open
a file selector for you to choose a name if the document was not
previously saved before.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > Saving a Document
Save
As
Saves the document in the active document window under a different
name.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > Saving a Document
Save
As Template
Saves the document in the active document window as a template,
which will open in an unnamed window, protecting the original
document from being overwritten by saving it in PageStream.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > Saving a Document > Saving as a template
Revert
Reverts the document to its last saved status. This is the same
as closing a document without saving it and then re-opening it.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > Saving a Document > Revert
Save
as PDF
Opens the Save as PDF dialog box which provides control over the
creation of a PDF file representation of the current document
for use in distribution on the Internet and for electronic documentation.
See: Printing > Creating Documents for the World Wide Web > Saving a PageStream document as a PDF File
Collect
for Output
Saves the document in the active document window in a new folder
and under a possible new name, and copies all external graphic
items to that same folder.
See: Printing > Printing on an Imagesetter > Using a Service Bureau > Collect for Output
Insert
Text
Inserts a text file in the current text frame or text block. The
insertion point needs to be positioned for this command to be
available. Text filters will be used to import text from foreign
text formats.
See: Text > Typing and Importing Text > Importing Text > How to import text
Place
Graphic
Places a graphic in the document window. Graphic filters will
be used to import graphics in PageStream. Graphics may be made
external to save memory and drive space.
See: Objects > Graphics > Importing Graphics > How to import graphics
Export
Text
Exports the selected text to a file. Text filters will be used
to translate the text to foreign formats, but some attributes
may be lost unless you use PageStream's native IFF CTXT format.
See: Text > Typing and Importing Text > Exporting Text > How to export text
Export
Graphic
Exports the selected object(s) to a file. If a bitmap picture
is selected, suitable graphic formats will be presented. If another
PageStream object or several objects are selected, suitable drawing
formats will be suggested. In the latter case, it is recommended
to use PageStream's native IFF ILUS drawing format to avoid loss
of attributes.
See: Objects > Graphics > Exporting Graphics > How to export graphics
Acquire
Places a graphic in the document window from an attached scanner.
This option is dimmed when no Acquire modules are present.
See: Objects > Graphics > Importing Graphics > How to import graphics
Preferences
Opens the General Preferences dialog box, allowing you to customize
PageStream to your liking: autosave and autobackup options, revision
control, undo options, typographic aids, default language, default
font and size, default measurements, coordinates display, double
click options, duplicate and nudge offsets, interface view options,
zoom range, default folders to use, place graphic options, insert
text options, automatic text frame options, toolbox formats, drag
zoom options, default shape attributes, text frame transparency
and toolbar configuration.
System
Preferences (Amiga only)
Under AmigaOS, allows you to install font drawers, choose "send
to editor" scripts and select the screenmode used to run
PageStream.
See: Getting Started > Customizing PageStream > Amiga System Preferences
Print
Setup
Opens the Print Setup dialog box, allowing you to set up the printing
options specific to the printer selected. Under MacOS, the system's
print setup options for the connected printer will appear. Under
AmigaOS, a custom print setup requester is presented. In these
dialog boxes, you generally choose the printer port, whether you
print to the printer or an external file, the printer resolution,
the paper size and orientation, the dither method, etc.
See: Printing > Print Setup
Print
Opens the Print dialog box, allowing you to print the document
in the active document window. In this dialog box, you choose
the number of copies you want to print, the page range, the print
method used (greyscale, color, color separations, process separations,
spot separations), the scale used (actual size, thumbnails, scale
to fit, custom %), tiling options, and other miscellaneous options
(collate copies, reverse order, print blank pages, print pictures,
printers' marks, emulsion down, negative).
See: Getting Started > Printing, Printing > Printing on a Desktop Printer, Printing > Printing on an Imagesetter and Printing > Printing Color Separations
Quit
Closes all document windows and quits PageStream. You will be
prompted to save changes for every modified document.
Undo
Undoes the last action performed in the active document window.
See: Getting Started > Customizing PageStream > The General Tab > Undo
Redo
Cancels the previous Undo operation.
See: Getting Started > Customizing PageStream > The General Tab > Undo
Cut
Cuts the selection to the clipboard. The selection will be deleted
from the document.
See: Objects > Copying and Pasting Objects and Text > Copying and Pasting Text
Copy
Copies the selection to the clipboard. This will not affect the
document.
See: Objects > Copying and Pasting Objects and Text > Copying and Pasting Text
Paste
Pastes the contents of the clipboard into the document. If it's
a picture and the insertion point is positioned in a text frame,
the picture will be anchored to the text.
See: Objects > Copying and Pasting Objects, Text > Copying and Pasting Text and Objects > Anchored Objects
Clear
Deletes the selection from the document. This will not affect
the contents of the clipboard.
See: Objects > Copying and Pasting Objects and Text > Copying and Pasting Text
Select
All
If the insertion point is positioned in a text frame or text block,
this command will select all the text in the article or text block.
If the Object tool is selected from the Toolbox, all the objects
on the page will be selected upon choosing that command.
Find/Change
Opens the Find/Change dialog box, allowing you to find and replace
text you type in the proper text controls. You can set up the
scope of the search to the current article, to the current chapter
or to the entire document. You may set up additional options like
searching only whole words, and ignoring the case or the accents.
You can also use special codes to search invisibles such as paragraph
marks, tabs, etc.
See: Text > Finding and Replacing Text
Find
Again
Finds the next occurrence of the text typed in the Find/Change
dialog box.
See: Text > Finding and Replacing Text
Change
Again
Replaces the next occurrence of the text according to the options
set in the Find/Change dialog box.
See: Text > Finding and Replacing Text
Find/Change Attributes
Opens the Find/Change Attributes dialog box, allowing you to select
text based on specified attributes, and then set specified attributes
for that selected text.
Check
Spelling
Opens the Check Spelling dialog box allowing you to check the
spelling of the whole document. From this dialog box, you may
replace an unknown word with one from a list of similar words
or add it to a custom dictionary if the word is valid. The speller
will automatically select the correct language for the selection.
Use the Language submenu of the Text menu to choose a language.
See: Text > Checking the Spelling
Lookup
Word
Opens a dialog box allowing you to look up a word in any of the
installed dictionaries. From this dialog box, you may also add
or remove words from the dictionaries.
See: Text > Checking the Spelling
Information
Displays information about the selected object, i.e., type of
graphic, object size, filename and whether it is external or not.
If the insertion point is in a text frame, it will indicate the
filename of the article (if applicable) and the word count. You
can type a name and description for the object or article. Additionally,
you can make an object external or internal by checking or unchecking
the Leave External box.
Send
to Editor (Amiga only)
If the insertion point is positioned in a text frame or text block,
plays the script selected in System Preferences allowing to send
the text to the target text editor (normally PageLiner). If a
bitmapped picture is selected, plays the script selected in System
Preferences allowing to send the bitmapped picture to the target
graphic editor (normally BME). If a drawing is selected, plays
the script selected in System Preferences allowing to send the
drawing in the target drawing editor (a script is provided for
ProVector, but this is not installed by default).
See: Getting Started > Customizing PageStream > Amiga System Preferences > Editor preferences
Define
> Text Styles
Opens the Define Styles dialog box, allowing you to define the
text styles used in the current document. You may also append
styles from a PageStream document or style file, save the style
list as the default one, or save the style list to an external
file.
See: Text > Paragraph and Character Styles > Creating and Editing Styles
Define
> Object Styles
Opens the Define Styles dialog box, allowing you to define the
object styles used in the current document. You may also append
styles from a PageStream document or style file, save the style
list as the default one, or save the style list to an external
file.
Define
> Colors
Opens the Define Colors dialog box, allowing you to define the
colors available in the current document. You may also append
colors from a PageStream document or color file, save the color
list as the default one, or save the color list to an external
file.
See: Line, Fill and Color > Creating and Editing Colors > Creating and Editing Colors
Define
> Variables
Opens the Define Variables dialog box, allowing you to define
the variables available in the current document.
See: Text > Insert Variable > User Variables
Define
> Index Topics
Opens the Define Index Topics dialog box, allowing you to add,
edit and remove index topics and cross references. Index marks
can also be deleted.
Define
> Figure Types
Opens the Define Figure Types dialog box, allowing you to add,
edit and remove figure types. Figure marks can also be deleted.
See: Text > Large Document Publishing > Creating a Table of Figures
Define
> Kerning Pairs
Opens the Define Kerning dialog box, allowing you to set or override
the kerning for installed fonts.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Defining Custom Kerning Pairs
Define
> Hyphenation
Opens the Define Hyphenation dialog box, allowing you to add and
remove hyphenated words in the hyphenation exception dictionary
for the specified language.
See: Text > Paragraph Attributes > Define Hyphenation
Define
> Tracking Tables
Opens the Define Tracking dialog box, allowing you to define font
specific tracking tables to override the default tracking tables.
Define
> Font Substitution
Opens the Font Substitution dialog box, allowing you to choose
the fonts that will be substituted when a document containing
fonts not installed is opened. There are options to simply display
the fonts not present with the substituted fonts or to convert
them definitely to the new fonts specified. In the latter case,
font information built into the document will be changed.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > Opening a Document > Font substitution
Generate
> Index
Opens the Generate Index dialog box, allowing you to .
Generate
> Table of Contents
Opens the Generate Table of Contents dialog box, allowing you
to .
See: Text > Large Document Publishing > Creating a Table of Contents
Generate
> Table of Figures
Opens the Generate Table of Figures dialog box, allowing you to
.
See: Text > Large Document Publishing > Creating a Table of Figures
Master
Page Setup
Opens a dialog box allowing you to change the attributes of the
current master page, i.e., page size and orientation, margin and
column guides, and the double-sided and facing pages modes.
See: Documents > Master Pages
Page
Setup
Opens a dialog box allowing you to change the master page on which
the current page is based, and whether the master page objects
are shown in the front, shown in the back or not shown. You may
also assign a name and a description to the current page.
See: Documents > Master Pages > Master Page Objects > To change how master page objects are shown on a page
Document
Setup
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set up how the pages of the
document are numbered as a whole. You may also assign a name and
a description to the document.
See: Documents > Pagination
Chapter
Setup
This command is available only if chapters exist in the document.
It can be used to override document settings for the current chapter.
You may also assign a name and a description to the current chapter.
See: Documents > Pagination > Page Numbers in Chapter
Insert
Page
Inserts one or more pages. By default, the page(s) will be inserted
before the current page in the current chapter, but you may override
these settings with the pop-up menus in the Insert Page dialog
box. You can also select the master page to use for the newly
inserted page(s). Note that it is not necessary to insert pages
at the end of the document because PageStream automatically creates
new pages as you place objects on them.
See: Documents > Pages > Page Arrangement > Inserting pages
Delete
Page
Opens a dialog box allowing you to delete one or more pages. By
default, the current page will be selected in that dialog box.
See: Documents > Pages > Page Arrangement > Deleting pages
Move
Page
Opens a dialog box allowing you to move the specified page(s)
to another location and/or chapter.
See: Documents > Pages > Page Arrangement > Moving pages
Reports
Displays useful information about the current document. You can
choose the information to display in that dialog box (fonts, styles,
colors, external graphics, articles, revision history) and save
it to an external file.
Set
Grid
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set the grid spacing, offset,
display interval and snap-to-grid options.
See: Documents > Guides and the Grid > The Grid
Show/Hide
Grid
Shows or hides the grid.
See: Documents > Guides and the Grid > The Grid
Snap-to-grid
When this item is selected, the objects will be snapped to the
grid when moved or resized with the mouse.
See: Documents > Guides and the Grid > The Grid
Set
Page Guides
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set page guides for the specified
master page and side. You may also configure snap-to-guide options.
See: Documents > Guides and the Grid > Guides
Show/Hide
Guides
Shows or hides the page guides.
See: Documents > Guides and the Grid > Guides
Snap-to-guides
When this item is selected, the objects will be snapped to the
page guides when moved or resized with the mouse.
See: Documents > Guides and the Grid > Guides
Set
Rulers
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set the rulers' offset and
zero point, direction and measurement systems used horizontally
and vertically.
See: Documents > Rulers and Measurements > Changing the rulers
Show/Hide
Rulers
Shows or hides the rulers.
See: Documents > Rulers and Measurements > Changing the rulers
Create
Text Frames
Opens a dialog box allowing you to create automatically text frames
based on the column margins, number of columns and gutter specified.
Default values are taken from the current master page.
Link
Text Frames
After choosing that command, the mouse pointer will change to
an empty text frame shape. Clicking on a text frame will make
the mouse pointer change to a full text frame shape and indicate
where the text will be linked from. Clicking on another frame
will then link it to the frame you previously clicked on.
See: Text > Articles > Text Frame Links > Linking text frames
Unlink
Text Frames
The insertion point must be in a text frame for this command to
be available. This command will break links before and after the
text frame. If you want to unlink in only one direction, hold
down a Shift key before choosing the Unlink Text Frames command.
See: Text > Articles > Text Frame Links > Unlinking text frames
Font
Choose a font to apply to the selected or future text from this
submenu. AmigaOS users must choose a font from the Font requester
because AmigaOS does not support scrolling menus.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Fonts
Size
Choose a preset font size to apply to the selected or future text
from this submenu or choose Other to type a different size.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Size and Width
Width
Choose a preset font width to apply to the selected or future
text from this submenu or choose Other to type a different width.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Size and Width
Type
Style
Choose a type style to apply to the selected or future text from
this submenu. Hold down a Shift key while choosing a type style
to customize the style.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Type Styles
Attributes
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set up several typesetting
attributes at the same time. You can apply text and/or paragraph
styles, font used, text size and width, predefined or custom text
styles, and paragraph alignment. This dialog box also provides
shortcuts to the Leading, Kerning, Paragraph Format, Line &
Fill, Tracking, Hyphenation and Tabs dialog boxes to apply these
attributes all at the same time.
See: Text > Character Attributes, Text > Paragraph Attributes and Line, Fill and Color > Line and Fill Options
Line
& Fill
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set stroke and fill attributes
to the selected or future text. You may change the stroke's weight,
color, style and bitmapped pattern, as well as the fill color,
type (basic, gradient, radial and shape) and bitmapped pattern.
Finally, you can choose the screen type, frequency and angle to
use for each plate. Screens are only available to PostScript (and
halftone printing with AmigaOS).
Tracking
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set a predefined tracking table,
track amount, and character and word spacing to apply to the selected
or future text. You may also specify the last line flush zone
to force justify paragraphs depending on the space between the
right margin and the end of the last line.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Tracking
Leading
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set the leading type, amount
and mode of the selected or future text. You can also check the
Maintain Leading box to keep the lines aligned from column to
column when text wrap is set to objects positioned over the text
frame.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Leading
Tabs
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set tab stops for selected
or future text. You may set the tabs' type, position and fill
character. You can also set the default tab spacing.
See: Text > Paragraph Attributes > Tabs
Paragraph
Format
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set left, right and first line
indents, inter-paragraph spacing, paragraph alignment and paragraph
type (plain, bulleted or drop cap).
See: Text > Paragraph Attributes
Alignment
Choose a paragraph alignment to apply to the selected or future
text from this submenu.
See: Text > Paragraph Attributes > Alignment
Hyphenation
> Set Hyphenation
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set the hyphenation language
and rules: smallest word to hyphenate, minimum characters before
and after, maximum hyphens in a row and the size of the hyphenation
zone. You may also choose to hyphenate lowercase words only.
See: Text > Paragraph Attributes > Auto Hyphenation
Hyphenation
> Auto Hyphenation
Select this command to hyphenate words automatically.
See: Text > Paragraph Attributes > Auto Hyphenation
Hyphenation
> Insert Soft Hyphen
Inserts a soft hyphen (Unicode number 134). If the soft hyphen
falls into the hyphenation zone specified in the Set Hyphenation
dialog box, the word will be hyphenated at that position.
See: Text > Paragraph Attributes > Auto Hyphenation > To hyphenate one occurrence of a word
Hyphenation
> Remove Soft Hyphens
Removes the soft hyphens in the text selection.
See: Text > Paragraph Attributes > Auto Hyphenation
Kerning
> Set Kerning
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set the kerning and ligature
options for the selected or future text.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Auto Kerning and Ligatures
Kerning
> Auto Kerning
Select this command to kern text automatically.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Auto Kerning and Ligatures
Kerning
> Manual Kern
Opens a dialog box allowing you to kern the characters to the
left and right of the insertion point.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Manual Kerning
Kerning
> Remove Kerning
Removes manual kerning in the text selection.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Manual Kerning > To remove manual kerning
Language
Choose a language to apply to the selected or future text from
this submenu.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Language
Convert
Case
Choose from the commands in the submenu whether to convert the
selected text to uppercase, lowercase or capitalized.
See: Text > Character Attributes > Convert Case
Insert
> Character
Opens a dialog box allowing you to view the whole character set
of the selected font so that you can insert one in the text frame
or text block. This dialog box also allows you to view the Control-C
and Control-D mnemonics to insert the selected character directly.
See: Text > Typing and Importing Text > Typing Text > Inserting Characters Visually and Appendices > Special Characters
Insert
> Page #, Previous Frame Page #, Next Frame Page #, Page Count,
Chapter #, Chapter Count
Choose one of these commands to insert the corresponding variable
in the text frame or text block.
See: Text > Insert Variable
Insert
> Document Name, Chapter Name, Master Page Name, Page Name
Choose one of these commands to insert the document, chapter,
master page, or page name in the text frame or text block.
See: Text > Insert Variable
Insert
> Date, Time, Revision Number
Choose one of these commands to open a dialog box allowing you
to insert the corresponding variable in the format specified.
See: Text > Insert Variable > Date Variables and Text > Insert Variable > Time Variables
Insert
> Text Mark
Choose this command to insert a text mark at the insertion
point's current position. You will be asked to enter a name for
the text mark. This is useful for cross-referencing documents.
See: Text > Insert Variable and Text > Insert Variable > Using text marks for cross-referencing documents
Insert
> Text Mark Page #
Choose this command to insert the page number of one of the text
marks. You may choose the page number's format to use.
See: Text > Insert Variable and Text > Insert Variable > Using text marks for cross-referencing documents
Insert
> Text Mark Name
Choose this command to insert the name of one of the text marks.
See: Text > Insert Variable and Text > Insert Variable > Using text marks for cross-referencing documents
Insert
> Figure Mark
Choose this command to insert a figure mark at the insertion
point's current position. You will be asked to choose a figure
type catagory and enter a name for the figure mark.
See: Text > Insert Variable and Text > Large Document Publishing > Creating a Table of Figures
Insert
> Figure Number
Choose this command to insert the ordered number of one of the
figure marks.
See: Text > Insert Variable and Text > Large Document Publishing > Creating a Table of Figures
Insert
> Figure Page #
Choose this command to insert the page number of one of the figure
marks. You may choose the page number's format to use.
See: Text > Insert Variable and Text > Large Document Publishing > Creating a Table of Figures
Insert
> Figure Name
Choose this command to insert the name of one of the figure marks.
See: Text > Insert Variable and Text > Large Document Publishing > Creating a Table of Figures
Insert
> Variable Text
Opens the Define Variable String dialog box allowing you to create,
edit, remove and insert custom variables. This can be used for
mail merging documents.
See: Text > Insert Variable > User Variables
Insert
> Index Mark
Opens the Insert Index Mark dialog box allowing you to insert
a mark to an Index Topic.
Break
> Insert Column Break, Insert Page Break
Interrupts the text flow in the current column or page.
See: Text > Interrupting Text Flow
Paragraph
Styles
Choose a paragraph style to apply to selected or future text from
the submenu. Hold down a Shift key while choosing a style to modify
its attributes.
Text
Styles
Choose a text style to apply to selected or future text from the
submenu. Hold down a Shift key while choosing a style to modify
its attributes.
Line
& Fill
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set up stroke, fill and screen
options for the selected object(s). You can alter the stroke's
weight, color, style, bitmapped pattern, start and end types,
cap and join types, and the miter limit. Fill options include
basic, gradient, radial and shape fills, bitmapped patterns and
several taper types. Screen options include plate control, six
screen types, and frequency and angle control. Screens are only
available to PostScript (and halftone printing with AmigaOS).
Text
Wrap
Opens a dialog box allowing you to set text wrap options for the
selected object(s). You can choose to flow the text around the
shape or around the bounding box, using specified horizontal and
vertical offsets. You may also choose from six wrap methods.
See: Objects > Setting Object Attributes > Text Wrap
Duplicate
Duplicates the selected object(s). Copies will be offset from
the original(s) by the amounts specified in General Preferences.
See: Objects > Copying and Pasting Objects > Duplicating objects
Transform
Opens a dialog box allowing the selected object(s) to be duplicated,
moved, scaled and rotated a specified number of times with the
values specified in the corresponding text controls. It is a powerful
step-and-repeat feature with additional flexibility.
Rotate
Opens a dialog box allowing the selected object(s) to be rotated,
slanted and twisted by specified amounts.
See: Objects > Object Transformation > Rotating Objects
Align
Opens a dialog box allowing the selected object(s) to be aligned
to the left, center or right of either their bounding box, the
current page, the mouse position or the specified coordinates.
See: Objects > Aligning and Distributing Objects > Aligning Objects
Distribute
For this command to be available, at least two objects must be
selected. It opens a dialog box allowing you to distribute an
equal amount of space between the selected objects. Other options
include spacing equally the left edges, center axes or right edges
of the selected objects. Objects may be distributed horizontally
or vertically, either within their bounding box or using a specified
amount of space.
See: Objects > Aligning and Distributing Objects > Distributing Objects
Move
Opens a dialog box allowing you to move the selected object(s)
a specified amount of space, horizontally and/or vertically. An
option is provided to snap the object(s) to the grid and guides.
See: Objects > Moving Objects
Move
to Page
Moves the selected object(s) to another page and/or chapter.
See: Objects > Moving Objects > To move an object to another page
Join
Objects
For this command to be available, at least two objects must be
selected. It joins the objects together, making a transparent
hole at the areas where they overlap. Objects retain their attributes
when joined together to form a compound object.
Merge
Paths
For that command to be available, at least two objects must be
selected. It merges the objects together, making a transparent
hole at the areas where they overlap. It also converts the objects
to paths, so the new composite path becomes editable with
the Reshape tool. Splitting the merged objects will split the
components into individual paths; they will no longer be editable
shapes.
Split
Splits a compound object or a composite path.
See: Objects > Compound Objects and Composite Paths > Splitting compound objects and composite paths
Convert
to Path
Converts the selected object(s) to paths so that they can be edited
with the Reshape tool. Text blocks can be converted to paths with
the TextFX extension.
See: Objects > Creating Graphics and Appendices > Extensions > TextFX > Converting text to paths
Drawing
> Make Drawing
Creates a drawing from the selected object(s).
See: Objects > Using Objects > Working with Drawings and Objects > Layers
Drawing
> Dissolve Drawing
Dissolves a selected drawing into separate components so that
they can be edited. Objects inside drawings can also be edited
while still inside the drawing using the Layer Palette.
See: Objects > Using Objects > Working with Drawings and Objects > Layers
Drawing
> Add to Drawing
Adds the selected object(s) to the selected drawing.
See: Objects > Using Objects > Working with Drawings and Objects > Layers
Group
For that command to be available, at least two objects must be
selected. It groups the selected objects so that they can be moved,
scaled, etc. together.
See: Objects > Using Objects > Working with Groups
Ungroup
Ungroups the selected group.
See: Objects > Using Objects > Working with Groups
Lock
Locks the selected object(s). This prevents them from being moved,
scaled, etc.
See: Objects > Editing Objects > To lock an object
Unlock
Unlocks the selected object(s).
See: Objects > Editing Objects > To lock an object
Stack
> Bring to Front, Bring Forward, Send to Back, Send Backward
Brings the selected object(s) to the front or one level forward,
or sends the selected object(s) to the back or one level backward.
See: Objects > Using Objects > Changing the stack order of objects
Frame
> None
Converts a text frame to an ordinary PageStream shape or path.
Frame
> Text
Converts any text shape or path to a shaped text frame. Generally
used to create shaped text frames.
See: Text > Putting Text on the Page > Creating Text Frames > To convert a shape or path into a text shape frame
Frame
> Text Frame Options
Sets the number of columns and gutter space for the selected text
frame(s) and left, right, top and bottom margins.
See: Text > Putting Text on the Page > Creating Text Frames > To change the number of columns in a text frame after creating it
Mask
> Mask Graphic
For that command to be available, one bitmapped picture and an
overlapping shape or path must be selected. It crops the picture
around the shape so that the shape appears to be filled with the
picture.
See: Objects > Masks > Masking Graphics
Mask
> Release Mask
Releases the shape used to mask a bitmapped picture.
See: Objects > Masks > Masking Graphics > To unmask a masked graphic
Mask
> Clear Mask
Clears the shape used to mask a bitmapped picture.
See: Objects > Masks > Masking Graphics > To unmask a masked graphic
Mask
> Generate Mask
Generates a clipping fence around the non-white parts of a bitmapped
picture so that the text can flow around the subject of the picture.
See: Objects > Masks > Generating a Mask Automatically
Styles
Choose an object style to apply to the selected object(s) from
the submenu. Hold down a Shift key while choosing a style to modify
its attributes.
See: Objects > Object Styles
Play
External Script
Opens a file selector allowing you to choose an external ARexx
or AppleScript to play.
See: Scripting > What are Scripts?
Start
Recording
Starts recording every subsequent action in PageStream.
See: Scripting > What are Scripts?
Stop
Recording
Stops recording a script. A dialog box will open allowing you
to manually edit the script, assign a name to it, display it in
the Scripts menu and assign a hotkey combination to it.
You may hold down a Shift key while choosing a script from the Scripts menu to change the options for this script.
See: Scripting > What are Scripts?
View
Choose a view magnification level from the submenu to change the
magnification of the page in the current window.
See: Getting Started > Navigating a Document > Changing View Magnifications
Bookmarks
Opens the Bookmarks dialog box where bookmarks can be inserted
into the text, and display text where existing bookmarks.
See: Getting Started > Navigating a Document > Changing View Magnifications
Show/Hide
Toolbox
Shows or hides the Toolbox.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > The PageStream Screen > Toolbox and the Toolbox section of this table of contents
Show/Hide
Toolbar
Shows or hides the Toolbar.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > The PageStream Screen > Toolbar
Show/Hide
Edit Palette
Shows or hides the Edit Palette.
See: Text > Formatting Text > Applying Text Attributes with the Edit Palette, Objects > Editing Objects and the Edit Palette section of this table of contents
Show/Hide
Color Palette
Shows or hides the Color Palette.
See: Line, Fill and Color > Applying Line, Fill and Color Attributes > The Color Palette and the Color Palette section of this table of contents
Show/Hide
Style Palette
Shows or hides the Style Palette.
See: Text > Paragraph and Character Styles and the Style Palette section of this table of contents
Show/Hide
Script Palette
Shows or hides the Script Palette.
See: Scripting > What are Scripts? and the Script Palette section of this table of contents
Show/Hide
Page Palette
Shows or hides the Page Palette.
See: Documents > Pages and the Page Palette section of this table of contents
Show/Hide
Document Palette
Shows or hides the Document Palette.
See: Documents > Chapters, Documents > Master Pages and the Document Palette section of this table of contents
Remember
Window Positions
Saves the window positions in the PageStream preferences file,
making these windows open at the new positions in the future.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > The PageStream Screen > Customizing your screen
New
Window
Displays a new view of the active document in a new window.
See: Getting Started > Document Window
Hide
Window
Hides the window selected from the submenu.
See: Getting Started > Document Window
Show
Window
Choose a window to show from the submenu. Hold down a Shift key
while choosing the window's name to select additional display
options, such as Greyscale, Color or Color Separations displays.
In the latter case, choose the plate to display from the pop-up
menu and whether the color is overprinted or not. This dialog
box also allows you to rename the document view.
See: Getting Started > Document Window
Help
Displays the online help system.
See: HHV User Manual
About
Displays information about PageStream, its authors, GrasshopperLLC's
contact information, the license owner's name and his or her registration
number. The location varies between platforms.
PageStream allows you to open an unlimited number of documents at once, each one with an unlimited number of views. It also allows you to set up various display options, such as Greyscale mode and Preview Color Separations.
See: Getting Started > Document Window
The controls to the bottom left of the document window allow you to change the view magnification level and navigate the document (switch pages and chapters, and display master pages).
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > The PageStream Screen > View and Page Controls
Some of PageStream's controls may be set to an indeterminate state when attributes conflict to avoid changing them accidentally.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > The PageStream Screen > Indeterminate state of controls
PageStream's window positions may be saved in the preferences file if you want the windows to open at specific positions at startup.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > The PageStream Screen > Customizing your screen
The Navigator window will appear at startup and when all document windows are closed. It provides shortcuts to commonly used commands.
The Toolbar gives you easy access to commonly used commands. It can be configured via the Preferences dialog box. It may also be hidden to save screen space.
See: Getting Started > Exploring PageStream > The PageStream Screen > Toolbar
The Toolbox can be used to create and modify objects and text. Only one tool in it may be selected at the same time. Some tools are grouped together in a flyout tool group and may be hidden. To select one of these tools, click on the flyout tool group button (which has a small arrow to the top right of the button) and drag out from the Toolbox.
The Edit Palette allows you to format text and edit objects quickly and easily. It provides several shortcuts to the major object and text attributes, and it displays the coordinates of the selected object(s) or point(s) to modify them easily. Its contents vary depending on the context: tool selected in the Toolbox, object selected, mouse operation, etc. It is highly recommended to keep it displayed because it can speed up object editing and text formatting considerably. Additionally, some features such as TextFX are only available via the Edit Palette. The three major variants of the Edit Palette are shown below.
See: Objects > Editing Objects
See: Text > Formatting Text > Applying Text Attributes with the Edit Palette > Character view
See: Text > Formatting Text > Applying Text Attributes with the Edit Palette > Paragraph view
The Color Palette allows you to apply conveniently stroke and fill colors to text and objects, and enables you to edit the colors used in the document.
See: Line, Fill and Color > Applying Line, Fill and Color Attributes > The Color Palette
The Style Palette allows you to apply paragraph and character styles to the selected text and object styles to the selected objects, as well as edit the existing text and object styles.
See: Text > Paragraph and Character Styles and Object > Object Styles
The Script Palette allows you to record and play internal scripts, as well as edit the existing scripts.
See: Scripting > What are Scripts?
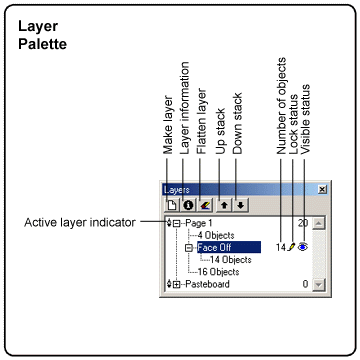
The Layer Palette allows you to set the active drawing layer for the page, make layers/drawings invisible and visible, shortcuts for creating and deleting layers, and shortcuts for changing the stack order of layers.
The Page Palette allows you to move the pages in your document, create and dissolve page spreads, change the master page on which a page is based, and insert or delete pages.
The Document Palette allows you to change the document's structure: add, move, insert, delete and edit chapters, and add, delete and edit master pages.
See: Documents > Chapters and Documents > Master Pages
PageStream's Topic Table of Contents
BME User Manual
PageLiner User Manual
SoftLogik Help System